Difference between revisions of "NumericPython"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
'''Numeric Python: Some handy array tools''' | '''Numeric Python: Some handy array tools''' | ||
| − | =Introduction= | + | =A Quick Introduction to Python= |
| − | =Getting Started= | + | Python is a high-level scripting language than can prove useful in a number of situations. On this page, we will mostly be looking at the array processing functions available through it's '''Numeric''' package. However, we'll start with a little taster of the core language by way of an introduction. Python has lots to offer to the scientific programmer, through the routines contained within it's '''Scientific''' and '''Numeric''' packages (offering a possible alternative to Matlab, IDL or R, for example), as well as it's visualisation tools. Python can also act as a flexible front-end to your Fortran or C routines. There are a number of very good online tutorials (such as [http://docs.python.org/tutorial], for example) |
| + | |||
| + | =Getting Started with the Interpreter= | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | =Using the Numeric Package= | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 51: | ||
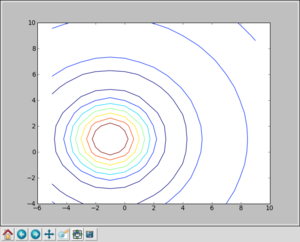
[[Image:Sinc-matplotlib-contour.png|thumb|300px|none|A contour map of the sinc function]] | [[Image:Sinc-matplotlib-contour.png|thumb|300px|none|A contour map of the sinc function]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | =Input and Output= | ||
Revision as of 09:18, 22 July 2009
Numeric Python: Some handy array tools
A Quick Introduction to Python
Python is a high-level scripting language than can prove useful in a number of situations. On this page, we will mostly be looking at the array processing functions available through it's Numeric package. However, we'll start with a little taster of the core language by way of an introduction. Python has lots to offer to the scientific programmer, through the routines contained within it's Scientific and Numeric packages (offering a possible alternative to Matlab, IDL or R, for example), as well as it's visualisation tools. Python can also act as a flexible front-end to your Fortran or C routines. There are a number of very good online tutorials (such as [1], for example)
Getting Started with the Interpreter
Using the Numeric Package
from Numeric import *
Arrays
More Interesting
x = arange(-5,10) y = arange(-4,11) z1 = sqrt(add.outer(x**2,y**2)) Z = sin(z1)/z1
If you have the NumTut package available, then you can simply type:
from NumTut import * view(Z)
and you should get a window similar to:
Otherwise, we can use the matplotlib package:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from pylab import meshgrid X, Y = meshgrid(x,y) plt.figure() plt.contour(X,Y,Z) plt.show()
and you should get a window similar to: